Understanding IELTS General Training Writing Task 1
IELTS General Training Writing Task 1 requires you to write a letter in response to a given situation. Unlike Academic Task 1, which focuses on describing visual data, General Training Task 1 tests your ability to communicate effectively in everyday written English situations.
Key Features:
- Time allocation: 20 minutes (recommended)
- Word count: Minimum 150 words
- Task type: Letter writing
- Scoring weight: Contributes to 1/3 of your overall Writing score
What Makes This Task Unique:
The task simulates real-life situations where you need to write letters for various purposes, from complaining about a service to inviting friends to a party. This practical approach tests your ability to communicate appropriately in different contexts.
Task Requirements and Assessment Criteria
Four Assessment Criteria:
1. Task Achievement (25%)
- Address all bullet points: Every task includes 3 bullet points that must be covered
- Appropriate tone: Match your writing style to the relationship with the recipient
- Sufficient detail: Provide adequate explanation and examples
- Letter purpose: Clearly state why you’re writing
2. Coherence and Cohesion (25%)
- Logical organization: Present ideas in a clear sequence
- Effective paragraphing: Use paragraphs to organize different points
- Linking devices: Use appropriate connectors and transitions
- Clear progression: Ideas should flow naturally from one to the next
3. Lexical Resource (25%)
- Vocabulary range: Use varied and appropriate vocabulary
- Precision: Choose words that convey exact meaning
- Collocations: Use natural word combinations
- Spelling accuracy: Maintain correct spelling throughout
4. Grammatical Range and Accuracy (25%)
- Sentence variety: Mix simple, compound, and complex sentences
- Tense consistency: Use appropriate tenses throughout
- Error frequency: Minimize grammatical errors
- Punctuation: Use correct punctuation marks
Scoring Bands:
Each criterion is scored from 0-9, and your Task 1 score is the average of these four scores, contributing to your overall Writing band score.
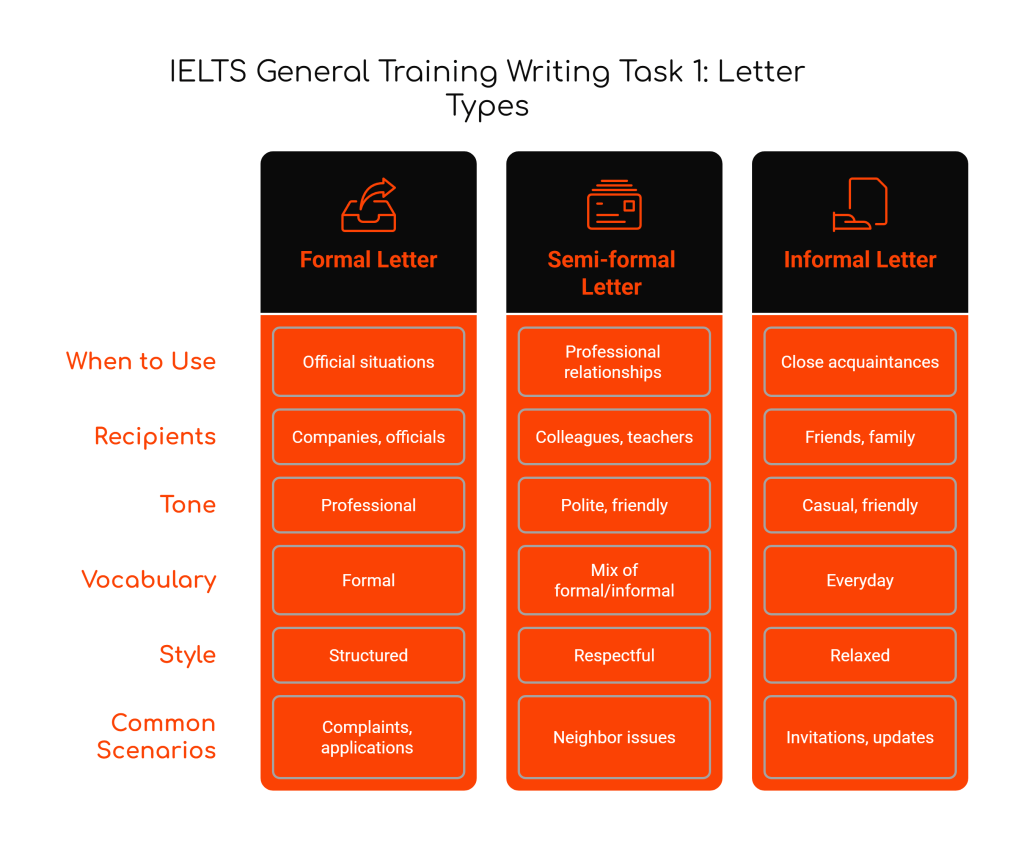
Types of Letters You’ll Encounter
1. Formal Letters
When to use: Writing to people you don’t know personally or in official situations Recipients: Companies, organizations, officials, landlords, managers Characteristics:
- Professional tone
- Formal vocabulary
- Structured approach
- Respectful language
Common scenarios:
- Complaints to companies
- Job applications
- Requests for information
- Official inquiries
2. Semi-formal Letters
When to use: Writing to people you know but maintain professional relationships with Recipients: Colleagues, neighbors, teachers, acquaintances Characteristics:
- Polite but friendly tone
- Mix of formal and informal language
- Respectful yet approachable
- Balanced formality
Common scenarios:
- Writing to neighbors
- Communicating with colleagues
- Contacting teachers or instructors
- Addressing service providers you know
3. Informal Letters
When to use: Writing to friends, family, and close acquaintances Recipients: Friends, family members, close colleagues Characteristics:
- Casual, friendly tone
- Everyday vocabulary
- Personal expressions
- Relaxed style
Common scenarios:
- Inviting friends to events
- Thanking family members
- Sharing news with friends
- Making arrangements with close contacts
Essential Structure and Format
Standard Letter Format:
Opening:
Dear [Name/Title],
Body Paragraphs:
- Paragraph 1: State your purpose for writing
- Paragraph 2: Address first bullet point
- Paragraph 3: Address second bullet point
- Paragraph 4: Address third bullet point
- Final Paragraph: Closing remarks and next steps
Closing:
Formal: Yours faithfully (if Dear Sir/Madam); Semi-formal: Yours sincerely (if Dear Mr./Ms. Name); Informal: Best regards, Kind regards, Best wishes, Love, Cheers
[Your name]
Paragraph Development Strategy:
Opening Paragraph (30-40 words):
- State your relationship to the recipient (if necessary)
- Clearly mention why you’re writing
- Set the appropriate tone
Body Paragraphs (30-40 words each):
- One main idea per paragraph
- Provide specific details and examples
- Use appropriate linking words
- Maintain consistent tone
Closing Paragraph (20-30 words):
- Summarize key points if necessary
- Suggest next steps or actions
- End with appropriate pleasantries
Language and Tone Guidelines
Formal Language Features:
Vocabulary:
- Use sophisticated, professional words
- Avoid contractions (don’t → do not)
- Choose precise, formal expressions
- Use passive voice when appropriate
Examples:
- “I am writing to express my dissatisfaction…”
- “I would be grateful if you could…”
- “I look forward to your prompt response”
- “Please do not hesitate to contact me”
Phrases for Different Purposes:
Complaining: “I am writing to complain about…”, “I am extremely disappointed with…” Requesting: “I would appreciate it if…”, “Could you please provide…” Apologizing: “I sincerely apologize for…”, “Please accept my apologies for…”
Semi-formal Language Features:
Balanced Approach:
- Mix formal and casual expressions
- Use some contractions moderately
- Maintain politeness with warmth
- Include personal touches
Examples:
- “I hope you’re doing well”
- “I would really appreciate your help with…”
- “Thanks for your time and consideration”
- “I hope to hear from you soon”
Informal Language Features:
Casual Elements:
- Use contractions freely
- Include colloquial expressions
- Show emotion and personality
- Use familiar vocabulary
Examples:
- “How’ve you been?”
- “Guess what happened!”
- “Can’t wait to see you!”
- “Hope everything’s going great”
Step-by-Step Writing Process
Step 1: Analyze the Task (2-3 minutes)
- Identify the letter type: Formal, semi-formal, or informal
- Determine your relationship with the recipient
- Highlight the three bullet points you must address
- Plan your tone and vocabulary level
Step 2: Plan Your Response (3-4 minutes)
- Decide on opening and closing phrases
- Allocate bullet points to paragraphs
- Think of specific details for each point
- Consider word count distribution
Step 3: Write Your Letter (12-13 minutes)
- Start with proper formatting
- Write opening paragraph with clear purpose
- Develop body paragraphs with specific details
- Include appropriate closing
- Check bullet point coverage
Step 4: Review and Edit (2-3 minutes)
- Count words (aim for 160-180)
- Check grammar and spelling
- Verify tone consistency
- Ensure all bullet points are addressed
Formal Letters: Complete Guide
When to Write Formal Letters:
- Complaints to companies or organizations
- Job applications or professional inquiries
- Requests to government departments
- Communication with landlords or property managers
- Official requests for information or services
Essential Formal Phrases:
Opening:
- “I am writing to complain about…”
- “I am writing to inquire about…”
- “I am writing with regard to…”
- “I am writing to apply for…”
Explaining Problems:
- “I am extremely disappointed with…”
- “I encountered several issues with…”
- “The service/product did not meet my expectations because…”
- “I was surprised to discover that…”
Making Requests:
- “I would be grateful if you could…”
- “Could you please arrange for…”
- “I would appreciate it if you would…”
- “Please ensure that…”
Expressing Dissatisfaction:
- “I find this situation completely unacceptable”
- “This has caused considerable inconvenience”
- “I expect better service from a company of your reputation”
- “I am not satisfied with the response I received”
Suggesting Solutions:
- “I would suggest that you…”
- “One possible solution would be to…”
- “I recommend that you consider…”
- “I propose that…”
Closing:
- “I look forward to your prompt response”
- “I expect to hear from you within [timeframe]”
- “Please resolve this matter as soon as possible”
- “I trust you will give this matter your immediate attention”
Sample Formal Letter Structure:
Complaint Letter Example Framework:
- Opening: State you’re writing to complain and briefly mention the issue
- Problem Description: Explain what went wrong with specific details
- Impact/Consequences: Describe how this affected you
- Requested Action: Clearly state what you want them to do
- Closing: Express expectation for quick resolution
Semi-formal Letters: Complete Guide
When to Write Semi-formal Letters:
- Communication with neighbors about issues
- Writing to colleagues about work-related matters
- Contacting teachers or course instructors
- Addressing service providers you have a relationship with
- Writing to acquaintances for favors or information
Balancing Formality and Friendliness:
Appropriate Phrases:
- “I hope this letter finds you well”
- “I would really appreciate your help with…”
- “I hope you do not mind me writing to you about…”
- “Thanks so much for your time and consideration”
Tone Characteristics:
- Polite but not overly formal
- Warm but professional
- Direct but respectful
- Personal but appropriate
Sample Semi-formal Scenarios:
Neighbor Relations:
- Noise complaints
- Shared facility issues
- Community events
- Property boundary matters
Workplace Communication:
- Project collaboration requests
- Schedule change notifications
- Resource sharing
- Social event invitations
Educational Context:
- Course information requests
- Meeting arrangements
- Assignment clarifications
- Recommendation requests
Informal Letters: Complete Guide
When to Write Informal Letters:
- Inviting friends to personal events
- Thanking family members for gifts or help
- Sharing personal news and updates
- Making casual arrangements with friends
- Apologizing to close friends for personal matters
Informal Language Features:
Contractions and Casual Grammar:
- “I’m”, “you’re”, “we’ll”, “can’t”, “won’t”
- Shorter, simpler sentences
- Questions for engagement
- Exclamation marks for emotion
Personal Expressions:
- “Hope you’re doing great!”
- “Can’t believe it’s been so long!”
- “You’ll never guess what happened!”
- “Miss you loads!”
Casual Vocabulary:
- “awesome”, “fantastic”, “amazing”
- “loads of”, “tons of”, “heaps of”
- “catch up”, “hang out”, “get together”
- “by the way”, “anyway”, “guess what”
Sample Informal Letter Topics:
Social Invitations:
- Birthday parties
- Weekend gatherings
- Holiday celebrations
- Casual meetups
Personal Updates:
- Job changes
- Moving news
- Relationship updates
- Achievement sharing
Thank You Notes:
- Gift appreciation
- Help acknowledgment
- Hospitality thanks
- Support recognition
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Tone Inconsistency
Problem: Mixing formal and informal language inappropriately Example: Using “Dear Sir” then writing “Thanks loads!” Solution: Maintain consistent formality level throughout
2. Incomplete Bullet Point Coverage
Problem: Addressing only 2 out of 3 required points Example: Forgetting to suggest solutions when asked Solution: Check each bullet point is fully addressed
3. Inappropriate Openings and Closings
Problem: Wrong salutation-closing combinations Example: “Dear Sir/Madam” with “Best wishes” Solution: Learn correct formal/informal pairings
4. Word Count Issues
Problem: Writing significantly under or over 150 words Solution: Practice writing exactly 160-180 words consistently
5. Generic Content
Problem: Using vague, non-specific information Example: “I had problems” instead of specific details Solution: Always include specific examples and details
6. Grammar and Spelling Errors
Problem: Basic language mistakes affecting clarity Solution: Allow time for proofreading and practice common error patterns
7. Poor Organization
Problem: Ideas scattered without logical flow Solution: Use clear paragraph structure and linking words
8. Wrong Register for Recipient
Problem: Too casual with unknown recipients or too formal with friends Solution: Always identify your relationship with the recipient first
Sample Questions and Model Answers
Sample Question 1: Formal Complaint Letter
Question: You recently purchased a product online but when it arrived, it was damaged and not as described. Write a letter to the company. In your letter:
- Explain what you ordered and what was wrong with it
- Describe how this affected you
- Say what you would like the company to do
Model Answer:
Dear Sir or Madam,
I am writing to express my strong dissatisfaction with a recent purchase I made from your online store on March 15th, order number #GT789123.
I ordered a blue leather laptop bag advertised as “premium quality genuine leather” for $89.99. However, when the item arrived yesterday, I discovered several serious problems. Firstly, the bag was black, not blue as ordered. Secondly, the material appears to be cheap synthetic leather, not genuine leather as described. Most importantly, there was a large tear in the side pocket, making the bag completely unusable.
This situation has caused me considerable inconvenience as I specifically needed this bag for an important business trip next week. I have now had to spend additional time and money finding an alternative product at short notice. Furthermore, I feel completely misled by your product description and am disappointed with your quality control standards.
I would like you to provide a full refund of $89.99 and cover the return shipping costs. Additionally, I expect compensation for the inconvenience caused. I have attached photos of the damaged item and my original receipt.
I look forward to your immediate response and expect this matter to be resolved within seven working days.
Yours faithfully,
[Your name]
Word count: 178
Sample Question 2: Semi-formal Letter to Neighbor
Question: Your neighbor has recently started playing loud music late at night. Write a letter to your neighbor. In your letter:
- Explain the problem and how it affects you
- Suggest a solution
- Mention what you will do if the problem continues
Model Answer:
Dear Mrs. Smith,
I hope you are settling in well to your new apartment. I am writing about an issue that I hope we can resolve together amicably.
Over the past two weeks, I have noticed that music from your apartment has been quite loud, particularly during weeknights after 11 PM. While I certainly do not want to spoil your enjoyment of your new home, the volume makes it difficult for me to sleep, and I have to wake up early for work each morning. My bedroom wall is adjacent to your living room, which might explain why the sound carries so clearly.
I was wondering if you might consider lowering the volume after 10 PM on weeknights, or perhaps moving your music system to a different room? I completely understand that weekends are different, and I am happy to be more flexible about noise levels then. Alternatively, if you let me know when you are planning to have parties or gatherings, I could arrange to stay elsewhere those nights.
I really hope we can work this out between ourselves as I would prefer to maintain our good neighborly relationship. However, if the noise continues at the current level, I may need to speak with the building management about the situation.
Thanks so much for your understanding, and I look forward to hearing from you.
Yours sincerely,
[Your name]
Word count: 176
Sample Question 3: Informal Invitation Letter
Question: You are organizing a surprise birthday party for a mutual friend. Write a letter to another friend inviting them to the party. In your letter:
- Explain why you are organizing the party
- Give details about the party
- Ask them to help with something specific
Model Answer:
Hey Maria!
How are things going? I hope you’re not too stressed with your new job! I’m writing because I’m organizing something really special and I need your help.
You know how Alex has been feeling a bit down lately after his breakup? Well, his 30th birthday is coming up next month, and I thought we should throw him an amazing surprise party to cheer him up! He’s always been there for all of us, and I think he deserves to know how much we all care about him. Plus, turning 30 is a big deal!
I’ve booked the function room at Mario’s Restaurant for Saturday, April 15th, from 7 PM to midnight. I’ve invited about 25 people – basically everyone from our university group plus some of his work colleagues. The plan is to tell Alex we’re just going for a quiet dinner, then surprise him when we arrive! Mario’s will provide a buffet dinner and birthday cake, and I’ve organized a playlist of all his favorite songs from our college days.
Here’s where I really need your help – could you possibly pick up the photo collage from the print shop on Friday afternoon? I’ve created this massive collection of pictures from all our trips and parties over the years, but I’ll be stuck at work that day. I can text you the address and give you the reference number.
Let me know if you can make it – it won’t be the same without you! Also, please keep it absolutely secret – you know how hopeless Alex is with surprises!
Can’t wait to see his face when we all jump out and yell “Surprise!”
Love,
Jenny
Word count: 251
Note: This example is slightly over the typical length to demonstrate informal style, but in the exam, aim for 160-180 words.
Advanced Tips and Strategies
1. Time Management Mastery
- Practice the 20-minute limit religiously during preparation
- Allocate specific time slots: 3 minutes planning, 14 minutes writing, 3 minutes checking
- Use a timer during practice sessions
- Develop writing speed through regular practice
2. Vocabulary Enhancement Techniques
Build Context-Specific Vocabulary:
Complaint Vocabulary: dissatisfied, unacceptable, inconvenience, compensation, resolution Request Vocabulary: appreciate, grateful, assistance, cooperation, accommodation Invitation Vocabulary: delighted, celebration, gathering, attendance, occasion
Learn Collocations:
- “Express dissatisfaction” not “say dissatisfaction”
- “Prompt response” not “quick response”
- “Considerable inconvenience” not “big inconvenience”
3. Grammar Accuracy Strategies
Common Error Patterns to Watch:
- Article usage: “I am writing to complain about the service”
- Preposition accuracy: “I look forward to hearing from you”
- Tense consistency: Don’t switch between past and present randomly
Sentence Variety Techniques:
- Simple: “I am writing to complain about the service.”
- Compound: “I am writing to complain about the service, and I expect a full refund.”
- Complex: “Although I have been a loyal customer for five years, I am extremely disappointed with the service I received.”
4. Coherence and Cohesion Excellence
Effective Linking Words by Category:
Adding information: furthermore, additionally, moreover, also Contrasting: however, nevertheless, on the other hand, despite this Explaining: consequently, therefore, as a result, due to this Sequencing: firstly, subsequently, finally, in conclusion
Paragraph Linking Strategies:
- Reference previous paragraphs: “As mentioned above…”
- Create logical flow: “This leads me to my next concern…”
- Use transitional phrases: “Regarding your second question…”
Practice Exercises
Exercise 1: Tone Identification
Instructions: Read the following sentences and identify whether they are formal, semi-formal, or informal.
- “I would be grateful if you could provide me with further information.”
- “Thanks loads for your help with this!”
- “I hope you do not mind me asking, but could you possibly help me out?”
- “I am writing to express my dissatisfaction with the service I received.”
- “How’ve you been? It’s been ages since we last caught up!”
Answers: 1. Formal, 2. Informal, 3. Semi-formal, 4. Formal, 5. Informal
Exercise 2: Opening and Closing Matching
Instructions: Match the appropriate closing with each opening.
Openings: A. Dear Sam, B. Dear Sir or Madam, C. Dear Mr. Johnson,
Closings:
- Yours faithfully
- Love
- Yours sincerely
Answers: A-2, B-1, C-3
Exercise 3: Bullet Point Analysis
Practice Question: You want to join a local sports club. Write a letter to the club manager. In your letter:
- Introduce yourself and explain your interest
- Ask about membership fees and facilities
- Inquire about beginner classes
Task: Identify what type of letter this is and plan how you would address each bullet point.
Analysis:
- Letter type: Formal (writing to club manager you don’t know)
- Bullet 1: Personal introduction + sport interest/experience
- Bullet 2: Specific questions about costs and what’s included
- Bullet 3: Class schedules, skill levels, equipment needed
Exercise 4: Word Count Challenge
Instructions: Write a complete opening paragraph for the sports club question above in exactly 35-40 words.
Sample Answer: “I am writing to inquire about membership at your sports club. I have recently moved to the area and am very interested in joining a local tennis club to continue playing regularly.” (32 words – needs expansion)
Improved Version: “I am writing to inquire about membership opportunities at your sports club. Having recently relocated to the area, I am very interested in joining a local tennis club to continue playing the sport I have enjoyed for several years.” (38 words)
Final Preparation Checklist
One Month Before the Exam:
- Complete diagnostic practice test to identify weaknesses
- Create vocabulary lists for each letter type
- Practice writing one letter per day
- Review grammar rules for common errors
- Familiarize yourself with assessment criteria
One Week Before the Exam:
- Complete at least 5 full practice tests under timed conditions
- Review and memorize opening/closing phrase combinations
- Practice quick task analysis (2-3 minutes maximum)
- Confirm understanding of formal/semi-formal/informal distinctions
- Prepare template structures for each letter type
Day Before the Exam:
- Review common mistake patterns
- Practice one final letter with full time constraints
- Confirm word count targets (160-180 words)
- Review linking words and transition phrases
- Get adequate rest and avoid cramming
During the Exam:
- Read the question carefully and identify letter type
- Spend 3-4 minutes planning your response
- Check you’ve addressed all three bullet points
- Monitor your time (aim to finish with 2-3 minutes for checking)
- Count words to ensure you meet the minimum requirement
- Proofread for grammar, spelling, and tone consistency
Conclusion
Mastering IELTS General Training Writing Task 1 requires understanding the different letter types, practicing appropriate language for each register, and developing efficient time management skills. Success comes from consistent practice, attention to detail, and the ability to adapt your writing style to match the relationship with your recipient.
Remember that this task tests your practical communication skills in English-speaking environments. Focus on clarity, appropriateness, and completeness rather than trying to impress with overly complex language. With dedicated practice using the strategies and frameworks provided in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to achieve your target band score.
The key to success lies in regular practice, careful attention to task requirements, and maintaining consistency in tone throughout your letter. Use this guide as your roadmap, practice regularly with authentic materials, and approach the exam with confidence in your preparation.
Good luck with your IELTS General Training Writing Task 1!
#IELTSGuidePhil #IELTSWriting #GeneralTraining #IELTSTips #IELTSPreparation #IELTSExam #WritingSkills #IELTSLetterWriting #IELTSBand7 #EnglishProficiency #WorkAbroad

Leave a comment