If you’re aiming for Band 7 or higher in IELTS Writing and Speaking, mastering the art of academic caution—also known as hedging—is essential. Hedging allows you to express opinions with appropriate balance, precision, and formality, which is critical in academic communication.
What is Academic Caution (Hedging)?
Hedging is a language strategy used to express uncertainty, politeness, or caution. It helps writers and speakers avoid overgeneralizing, soften claims, or acknowledge limitations in arguments.
Instead of making bold, absolute statements, you show awareness of complexity or alternative perspectives.
Example:
Fast food causes obesity.
Fast food may contribute to obesity in some individuals.
Why is Hedging Important in IELTS?
Shows Critical Thinking
IELTS examiners reward responses that recognize nuance, complexity, and alternative viewpoints.
Enhances Formality
Hedging is a hallmark of academic and professional communication.
Prevents Overgeneralization
Sweeping statements often sound unrealistic or overly simplistic and reduce the quality of your argument.
Improves Lexical Resource and Grammatical Range
Using modal verbs, cautious adverbs, and structures like passive voice demonstrates high-level English skills.
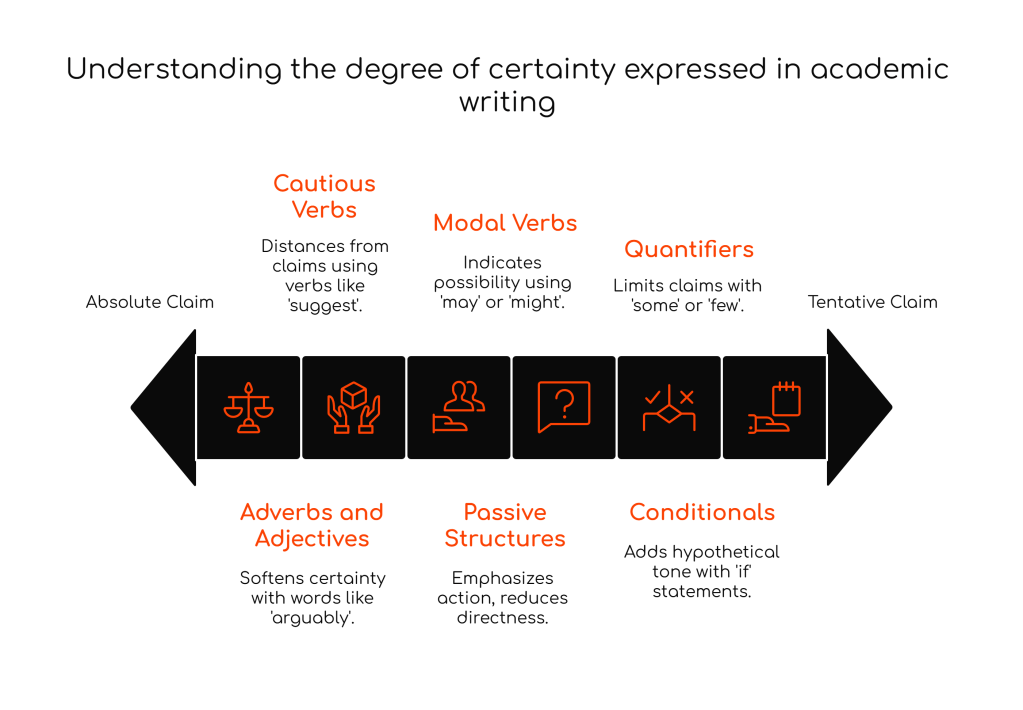
Types of Hedging
1. Modal Verbs
Used to indicate possibility or probability.
- may, might, can, could, would
This policy might improve public health outcomes.
2. Adverbs and Adjectives
Used to soften the degree of certainty.
- possibly, potentially, likely, unlikely, generally, arguably
It is arguably one of the most significant inventions.
3. Cautious Verbs
Used to distance yourself from absolute claims.
- suggest, indicate, appear, seem, imply
Research suggests that climate change may be accelerating.
4. Passive Structures
Used to emphasize the action over the agent and reduce directness.
It is believed that this policy will benefit the economy.
5. Quantifiers and Limiting Expressions
Used to show that a claim does not apply universally.
- some, many, a few, in most cases, to a certain extent
Some students may benefit from online learning.
6. Conditionals
Used to add hypothetical or cautious tone.
If implemented correctly, this law could reduce crime.
Hedging in IELTS Writing
Task 2 Example:
Advertising manipulates children.
Advertising may influence the decisions of children to some extent.
Academic Task 1 Example:
The number of tourists increased because of government policy.
The increase in tourists could be attributed to government initiatives.
Hedging in IELTS Speaking
In Speaking, excessive hedging is not necessary, but strategic softening can improve fluency and coherence.
Well, I suppose many people enjoy online shopping because it’s more convenient.
In my opinion, it might depend on the person’s lifestyle.
Common Mistakes
| Mistake | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Over-hedging | Makes your argument sound weak or unclear |
| No hedging | Sounds too absolute, especially in academic writing |
| Using incorrect modals | “It can happens…” instead of “It can happen…” |
| Confusing hedging with being vague | Be cautious, but still clear and well-reasoned |
Dos and Don’ts
| DO | DON’T |
|---|---|
| Use modal verbs appropriately | Avoid saying something “always” or “never” |
| Learn common hedging phrases | Don’t hedge every sentence |
| Practice with academic texts | Don’t confuse hedging with avoiding opinions |
| Apply hedging in conclusions too | Don’t make overconfident final statements |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is hedging required for Band 7+ in IELTS Writing?
Yes. Academic Writing values balance and nuanced thinking, which are reflected through hedging.
Q2: Can I hedge too much?
Yes. Over-hedging may weaken your argument. Use hedging where uncertainty is reasonable—not to avoid taking a stance.
Q3: Should I use hedging in IELTS Speaking?
Sparingly. Speaking is more informal, but phrases like “I think,” “maybe,” “I guess,” “it depends” are useful.
Top Strategies for IELTS Success
- Analyze model essays: Look for how expert writers hedge opinions or data.
- Practice transformation: Rewrite bold statements with hedging expressions.
- Build a hedging vocabulary bank: Include modal verbs, cautious adverbs, and impersonal structures.
- Mix sentence types: Combine hedged statements with clear evidence and examples.
- Get feedback: Ask your tutor or teacher if your hedging is balanced or excessive.
Sample Transformations
| Bold Statement | Hedged Version |
|---|---|
| Technology solves all problems. | Technology may help solve some problems. |
| Exercise prevents all illnesses. | Regular exercise can reduce the risk of many illnesses. |
| Online learning is better than traditional learning. | Online learning might be more effective for some learners. |
Common Hedging Phrases to Memorize
- It is possible that…
- There is a chance that…
- Some evidence suggests…
- It may be argued that…
- The data seems to indicate…
- To a certain extent…
- In most cases…
Final Thoughts
Mastering academic caution through hedging is an essential step toward achieving high IELTS Writing and Speaking band scores. It reflects your ability to think critically, communicate responsibly, and engage with academic topics in a nuanced and formal manner.
Whether you’re crafting a high-level Task 2 essay or expressing opinions during the Speaking test, hedging will set your language apart as mature, thoughtful, and academically appropriate.
Explore More with IELTS Guide Phil
Spotify Podcast:
IELTS Guide Phil on Spotify
Grammar and Writing Lessons:
Visit the full blog at ieltsguidephil.com
Join the Community:
- Facebook: IELTS Guide Phil
- X (Twitter): @ieltsguidephil
- BlueSky: @ieltsguidephil
#IELTSWriting #AcademicCaution #HedgingInEnglish #IELTSGrammar #IELTSBand7 #IELTSWithPhil #IELTSVocabulary #FormalEnglish #WritingTips #IELTS2025 #IELTS

Leave a comment